|
Adenokarzinom Lunge | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
| Last Update: 02.09.2019 | |
|
|
| Klassifikation | |
| ICD10: | C34.9 |
| ICD-O: | 8140/3 |
| Kategorie: | Neoplasie, maligne |
| Histolog. Typ: | Adenokarzinom |
| Immunphänotyp | |
| TTF1: + (80%) | CK7: + (70%) |
| Mutationen | |
| EGFR | |
| Altersverteilung | |
|
Lebensalter
|
|
| Links | |
Adenokarzinom der Lunge
Allgemeines:
-
Häufigster Typ den Lungenkarzinoms (USA ca. 40%)
-
Molekularbiolog. Adenokarzinome heterogen! 1
-
Geringste Assoziation zum Rauchen
-
Ca. 50% bei Diagnosestellung metastasiert (Lymphknoten, Gehirn, Knochen, Nebennieren)
Klinik:

Chondrosarkom
Epidemiologie:
Häufigster Subtyp den Lungenkarzinoms
-
(USA ca. 40%)
-
Häufigster Subtyp bei Frauen
und Nichtrauchern
-
Inzidenz ansteigend seit ca. 2000
Pathogenese:
This is the first item's accordion body. It is shown by default, until the collapse plugin adds the appropriate classes that we use to style each element. These classes control the overall appearance, as well as the showing and hiding via CSS transitions. You can modify any of this with custom CSS or overriding our default variables. It's also worth noting that just about any HTML can go within the
.accordion-body, though the transition does limit overflow.This is the second item's accordion body. It is hidden by default, until the collapse plugin adds the appropriate classes that we use to style each element. These classes control the overall appearance, as well as the showing and hiding via CSS transitions. You can modify any of this with custom CSS or overriding our default variables. It's also worth noting that just about any HTML can go within the
.accordion-body, though the transition does limit overflow.Makroskopie:
-
75% liegen peripher
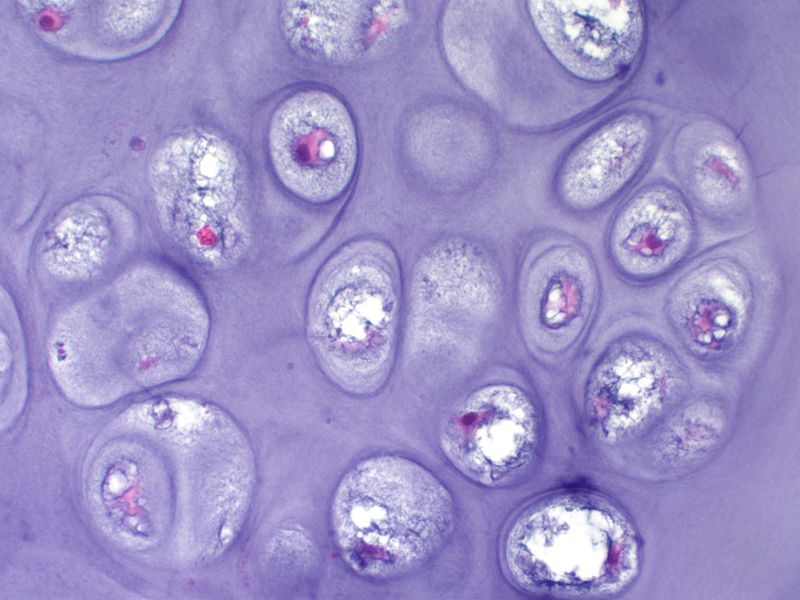
Mikroskopie:
-
variable Differenzierung:1
adenoid/drüsig, tubulär, papillär, 2
selten siegelringzelliges Wachstumsmuster
-
Zellen polygonal, kubisch bis zylindrisch
-
Zelldurchmesser ca. 13 µm,
Kerndurchmesser ca. 8 µm
-
bläschenförmige Zellkerne mit prominenten Nukleoli
-
granuläres Kernchromatin
-
vielfach zytoplasmatische Vakuolisierung als Zeichen der Mucinbildung
Zytologie:
Immunhistochemie:
Molekularpathologie:
hgigu
Differentialdiagnosen:
CK7Sonstiges:
Externe Links:
Patho-Pic {fa-share-square-o }
Quellen & weiterführende Literatur:
- 1 Longacre, T.A., Greenson, J.K., Hornick, J.L., & Reuter, V.E. (2022). Mills and Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology (7th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-1975150723.
- 2 Goldblum, J. R., Lamps, L. W., McKenney, J., & Myers, J. (2017). Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology - 2 Volume Set (11th Ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 978-0323263399.
Weiterführende Literatur:
- Goldblum, J. R., Lamps, L. W., McKenney, J., & Myers, J. (2017). Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology - 2 Volume Set (11th Ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 978-0323263399. (pp.123-344)
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Digestive system tumours. 5th ed. Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2019. (WHO classification of tumours series, vol. 1).
 Patienteninformation
Patienteninformation Anmerkung zu Gesundheitsthemen
Anmerkung zu Gesundheitsthemen